Understanding the Intricacies of Cardiac PET Scan Interpretation: A Comprehensive Guide
Guide or Summary:What is Cardiac PET Scan?Interpreting Cardiac PET Scan ResultsCase Studies and Real-World ApplicationsIn the realm of medical imaging, the……
Guide or Summary:
- What is Cardiac PET Scan?
- Interpreting Cardiac PET Scan Results
- Case Studies and Real-World Applications
In the realm of medical imaging, the Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan has emerged as a powerful tool for diagnosing and managing cardiovascular conditions. While PET scans are widely utilized across various medical specialties, their application in cardiac imaging offers a unique perspective on the heart's function and structure. This detailed guide delves into the nuances of cardiac PET scan interpretation, providing healthcare professionals with a comprehensive understanding of this sophisticated diagnostic technique.
What is Cardiac PET Scan?
A cardiac PET scan involves injecting a small amount of a radioactive substance, typically fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), into the patient's bloodstream. This substance is designed to highlight areas of increased metabolic activity within the heart. As the patient lies on a table, a PET camera captures images of the radioactive distribution throughout the heart. These images are then analyzed to assess the heart's blood flow, oxygen consumption, and glucose metabolism.
Interpreting Cardiac PET Scan Results
The interpretation of cardiac PET scan results requires a nuanced understanding of both the anatomy and physiology of the heart. Here are some key aspects to consider when interpreting cardiac PET scan images:
1. **Myocardial Perfusion Defects**: These defects indicate areas of the heart where blood flow is impaired. They can be caused by coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, or congenital heart defects. PET scans can help identify these defects by highlighting regions of reduced metabolic activity.
2. **Myocardial Viability**: Viability refers to the ability of heart muscle to contract effectively. PET scans can assess myocardial viability by evaluating the metabolic activity of the heart tissue. Areas of low metabolic activity may indicate poor viability, suggesting that these regions may be non-viable or scarred.
3. **Metabolic Imaging**: PET scans can also provide insights into the heart's metabolic activity. This information is crucial for diagnosing conditions such as diabetes mellitus, which can affect cardiac function. By measuring glucose metabolism, PET scans can help differentiate between ischemic and non-ischemic heart disease.
4. **Assessing Heart Function**: Beyond structural and metabolic assessments, cardiac PET scans can also evaluate the heart's overall function. This includes the assessment of systolic and diastolic function, which are critical for diagnosing conditions such as cardiomyopathy.

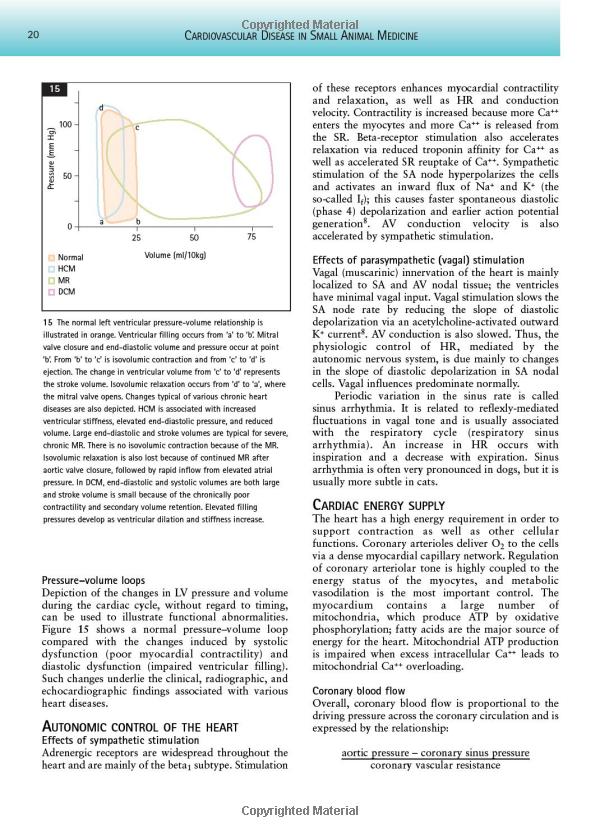
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
To illustrate the practical applications of cardiac PET scan interpretation, consider the following case studies:
1. **Coronary Artery Disease**: In a patient presenting with symptoms of chest pain, a cardiac PET scan revealed areas of myocardial perfusion defects, indicating a significant blockage in the coronary arteries. This finding led to timely intervention, preventing a potential myocardial infarction.
2. **Assessing Post-Myocardial Infarction Viability**: Following a myocardial infarction, a cardiac PET scan helped assess the viability of the infarcted region. By differentiating between viable and non-viable heart tissue, the scan guided the decision-making process regarding further interventions, such as coronary artery bypass grafting or percutaneous coronary intervention.
3. **Evaluating Heart Failure**: In a patient with symptoms of heart failure, a cardiac PET scan provided valuable insights into the patient's cardiac function and metabolism. This information was crucial for tailoring the treatment plan, including optimizing medications and recommending lifestyle modifications.

Cardiac PET scan interpretation is a sophisticated process that requires a deep understanding of both the heart's anatomy and physiology. By analyzing PET scan images, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into cardiac function, perfusion, and metabolism. This comprehensive guide has provided an overview of the key aspects to consider when interpreting cardiac PET scan results. As the field of medical imaging continues to evolve, cardiac PET scans will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular conditions.